

DOI:https://doi.org/10.46502/issn.1856-7576/2025.19.03.16
Eduweb, 2025, julio-septiembre, v.19, n.3. ISSN: 1856-7576
Cómo citar:
Zelenyi, V., Nahorna, K., Smolnykova, H., Atamanchuk, I., & Tkachenko, A. (2025). Developing leadership competencies in university students through project-based learning. Revista Eduweb, 19(3), 256-268. https://doi.org/10.46502/issn.1856-7576/2025.19.03.16
Desarrollo de competencias de liderazgo en estudiantes universitarios a través del aprendizaje basado en proyectos
Volodymyr Zelenyi
Department of Socio-Humanitarian Disciplines, Faculty of State Security, Kyiv Institute of the National Guard of Ukraine, Kyiv, Ukraine.
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1089-4314
Kateryna Nahorna
Department of Social Work and Rehabilitation, National University of Life and Environmental Sciences of Ukraine, Kyiv, Ukraine.
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-8099-9611
Halyna Smolnykova
Department of Science and Mathematics Education and Technologies, Borys Hrinchenko Kyiv Metropolitan University, Kyiv, Ukraine.
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5853-146X
Iurii Atamanchuk
Department of Education and Educational Institution Management, Classical Private University, Zaporizhzhia, Ukraine.
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1337-8013
Anna Tkachenko
Educational and Research Institute of Information and Educational Technologies, Bohdan Khmelnytsky National University of Cherkasy, Cherkasy, Ukraine.
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5326-1840
Recibido: 21/07/25
Aceptado: 20/09/25
Abstract
This study aimed to confirm the effectiveness of project methods in cultivating leadership skills among higher education students. The methodology encompassed a questionnaire survey and testing, specifically utilizing the Multifactor Leadership Questionnaire and the Situational Judgement Test. Measures of central tendency, including the arithmetic mean, median, and mode, were applied for data analysis. The study involved a sample size of 140 participants. Additionally, inductive statistical methods such as t-statistics, the Shapiro-Wilk test, and Cohen’s d were employed to analyze the data. The findings indicate that students in the experimental group demonstrated a higher level of leadership qualities, notably in communication (4.7 vs. 4.2) and confidence (4.8 vs. 4.3). Statistically significant differences were observed for the individual approach (t=2.1, p<0.05) and result orientation (t=2.4, p<0.05), thereby confirming the effectiveness of project methods. Key improvements were particularly evident in communication, confidence, and result-oriented skills, underscoring the efficacy of project-based methodologies in higher education. In conclusion, project methods positively influence the development of students’ leadership qualities, yielding superior outcomes in the experimental group compared to traditional approaches.
Keywords: active learning, building competencies, innovative education, pedagogical technology, project methods.
Resumen
Este estudio tuvo como objetivo confirmar la efectividad de los métodos de proyecto en el cultivo de habilidades de liderazgo entre estudiantes de educación superior. La metodología abarcó una encuesta y pruebas de cuestionario, específicamente utilizando el Cuestionario de Liderazgo Multifactorial y la Prueba de Juicio Situacional. Se aplicaron medidas de tendencia central, incluyendo la media aritmética, la mediana y la moda, para el análisis de datos. El estudio involucró un tamaño de muestra de 140 participantes. Además, se emplearon métodos estadísticos inductivos como las estadísticas t, la prueba de Shapiro-Wilk y la d de Cohen para analizar los datos. Los hallazgos indican que los estudiantes en el grupo experimental demostraron un mayor nivel de cualidades de liderazgo, notablemente en comunicación (4.7 vs. 4.2) y confianza (4.8 vs. 4.3). Se observaron diferencias estadísticamente significativas para el enfoque individual (t = 2.1, p < 0.05) y la orientación a resultados (t = 2.4, p < 0.05), confirmando así la efectividad de los métodos de proyecto. Las mejoras clave fueron particularmente evidentes en la comunicación, la confianza y la orientación a resultados, lo que subraya la eficacia de las metodologías basadas en proyectos en la educación superior. En conclusión, los métodos de proyectos influyen positivamente en el desarrollo de las cualidades de liderazgo de los estudiantes, obteniendo resultados superiores en el grupo experimental en comparación con los enfoques tradicionales.
Palabras clave: aprendizaje activo, construcción de competencias, educación innovadora, métodos de proyecto, tecnología pedagógica.
Introduction
The relevance of the issue under research is determined by the growing demands of the modern labour market for specialists who combine professional knowledge with universal skills. Today, employers expect employees not only to have technical competencies, but also the ability to effectively manage processes and people. Leadership qualities are becoming an important factor in success in a dynamic professional environment that requires adaptability and strategic thinking (Sviatko, 2024).
There is a growing interest in educational practice towards the implementation of project methods as an approach to training students, which contributes to the development of professional competencies and leadership qualities (Melguizo-Garín et al., 2022). This is particularly important in the context of higher education in Ukraine, where economic and societal transformations demand specialists capable of strategic decision-making and effective teamwork. In view of globalization and constant transformation of the labour market, society needs specialists who are able to effectively organize teamwork, make strategic decisions, etc. The needs of the labour market emphasize the relevance of research aimed at studying the impact of project-based learning on the development of students’ leadership qualities (Tretiak et al., 2021).
Leadership qualities are now a key element of successful professional activity (Breaugh et al., 2023). Leadership includes a wide range of competencies: communication skills, the ability to motivate others, strategic thinking and the ability to work in multifunctional teams. In the Ukrainian context, these qualities are particularly vital due to the rapid shifts in organizational structures and work environments. These qualities enable specialists to achieve professional goals, but also to ensure the development and sustainability of the organization in which they work (Ince, 2023).
Higher education institutions (HEIs) play a crucial role in the development of leadership qualities, as the prerequisites for the development of personal potential are created during the student years. The Ukrainian education system faces the challenge of modernizing its approaches to meet global standards, making the integration of innovative methods such as project-based learning particularly relevant. Project-based methods that combine theoretical knowledge with practical activities are one of the most effective tools for the development of leadership in HEIs (Birdman et al., 2022). The project-based approach contributes to the development of students’ leadership qualities, such as responsibility, the ability to act under uncertain conditions, etc. (Naseer et al., 2025).
The problem of the study is the poorly studied effectiveness of project-based methods for the development of leadership qualities. Despite numerous studies confirming the advantages of the project-based approach, there is also data indicating the limited impact of such methods in certain conditions (Williamson, 2023). This highlights the necessity of exploring how project-based learning methods can be adapted to the unique socio-economic and cultural conditions of Ukrainian higher education. The aim is to theoretically substantiate and empirically confirm the effectiveness of using project-based learning methods to develop leadership skills in higher school students. The study examines key variables such as communication skills, emotional intelligence, and decision-making abilities to evaluate their development through project-based methods. These variables were selected as they represent core leadership competencies required in dynamic and multidisciplinary professional environments. The aim involves the fulfilment of the following research objectives:
This article is structured into seven main sections. Following the abstract, the introduction establishes the relevance of developing leadership competencies in students and outlines the study's objectives. A comprehensive literature review then synthesizes existing theories of leadership and prior research on project-based learning (PBL), identifying key gaps that this study aims to address. The methods and materials section details the quasi-experimental research design, participant sampling, and the specific instruments used for data collection and analysis. The results section presents the empirical findings, comparing the development of leadership qualities between the control and experimental groups through descriptive and inferential statistics. Subsequently, the discussion interprets these results, contextualizing them within the broader academic discourse and acknowledging the study's limitations. The article concludes by summarizing the key findings and their implications in the conclusions section, followed by a complete list of bibliographic references containing the self-assessment questionnaire used in the research.
Literature Review
Leadership is a multi-aspect social phenomenon, which remains an object of researchers’ interest, as it determines the dynamics of the society development. According to Bhat et al. (2024), leadership should be considered not only as the ability of one person to influence others. It is a process that encompasses team development, the formation of common goals, and the creation of conditions for achieving effective results. We agree with the researchers’ statement and propose to consider the development of leadership as an integrated process.
Barner-Rasmussen et al. (2024) argue that classical leadership theories lay the foundation for understanding this phenomenon. They focus on such aspects as personality traits, leader behaviour, and the dependence of its effectiveness on the situational context. According to Gring-Pemble et al. (2024), behavioural theories emphasize actions that ensure the organization and motivation of the group. Situational approaches add the perspective of adaptation: leadership becomes effective only if the context and needs of subordinates are taken into account. In their book, Carducci et al. (2024) analysed modern leadership concepts, such as transformational, servant, and value-oriented. Transformational leaders inspire and develop their subordinates, servant leaders serve their interests, and value-oriented leaders unite the team with common moral principles. We agree with the researchers’ opinion and believe that effective leadership is possible only if the context of production tasks and the needs of the team are taken into account.
As Zhang & Ma (2023) emphasize, project-based learning methods are an effective tool for modernizing the educational process. They contribute to the development of students’ practical skills and key competencies. According to the researchers, they create conditions under which students are actively involved in solving real problems through the implementation of specific projects. The study of Riyanti et al. (2023) distinguishes the main approaches of project-based learning methods. They imply the integration of theoretical knowledge with practical experience, the interdisciplinary nature of tasks, result orientation, and cooperation in teams. The authors indicate that project-based methods are aimed at learning the material and developing students’ independence, responsibility, communication, and critical thinking. We support the position of the researchers and believe that project-based learning methods contribute to the development of key students’ competencies through practical activities.
Project activities play a key role in the educational process, as they contribute to the development of critical thinking through problem analysis and the search for optimal solutions. Huang et al. (2023) noted that it stimulates creativity, encouraging students to propose non-standard approaches and show initiative. According to the researchers, working in project teams develops skills of cooperation and effective communication, which are important aspects of training specialists for professional activity. We share the researchers’ position and are convinced that project activities contribute to the development of critical thinking, creativity, and team interaction. The opinion of Balleisen et al. (2024) that project-based learning methods are closely related to the development of leadership qualities, contributing to the development of key competencies is worth noting. They help students to acquire planning and organizational skills, make decisions under uncertain conditions, improve communication, motivate the team and work together. According to the authors, project activities contribute to the formation of responsibility and initiative, which is the basis of effective leadership. We agree with the researchers’ opinion and believe that project-based learning methods develop leadership qualities, contributing to the development of key competencies.
Research into the effectiveness of project-based learning methods for developing leadership skills has attracted considerable researchers’ attention. The analysis of Zahroh et al. (2023) shows that project activities contribute to the development of leadership skills. This is determined by the students’ involvement in teamwork, the distribution of roles and responsibilities, as well as the orientation towards achieving a specific result. The study of Safitri et al. (2024) emphasizes the importance of project methods for the formation of leadership competencies. In particular, the researchers focus on promoting the development of skills such as delegation of authority, team motivation, and the ability to adapt to change. We share the researchers’ opinion and believe that project methods contribute to the development of leadership skills through cooperation and distribution of responsibilities.
While most existing literature highlights the benefits of project-based methods (Hasanah et al., 2023); (Chang, 2021), critical gaps remain. Empirical studies such as Sviatko (2024) reveal contextual limitations, particularly in non-Western educational settings, where institutional support and teacher preparedness moderate outcomes. Similarly, Shekarian & Parast (2021) identify gender disparities in leadership skill acquisition, a factor underexplored in prior research. Pan et al. (2024) further emphasize the role of teacher training—a variable often overlooked in studies claiming universal efficacy.
This study addresses these gaps by (1) examining project-based methods in Ukrainian HEIs, a context with limited empirical coverage; (2) incorporating gender-disaggregated analysis; and (3) evaluating teacher support as a moderating factor. By testing the hypothesis (H₁) that project methods enhance leadership skills, we aim to provide nuanced insights beyond the dominant positive narrative.
Methods and materials
Research design
A quasi-experimental research design was developed. The research consisted of several stages. The duration and content of each stage are presented in Figure 1.
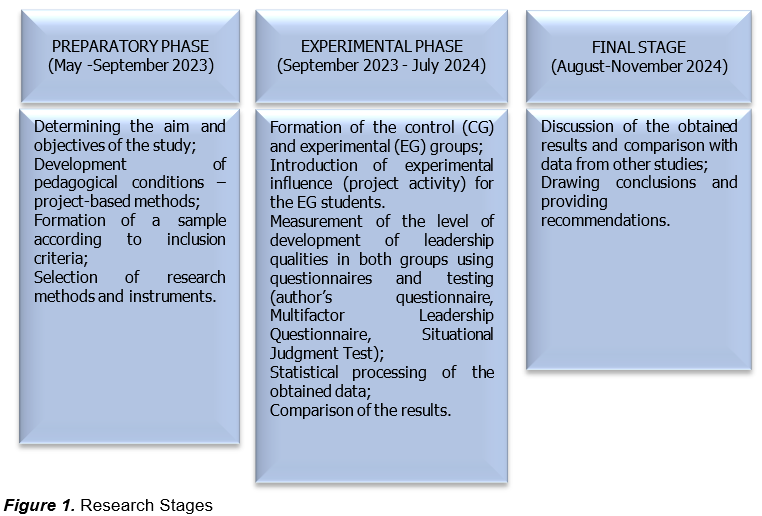
Sampling
The general population consisted of Ukrainian students. The sample included 3rd-year students of the National University of Life and Environmental Sciences of Ukraine (A), Faculty of Humanities at the Department of Social Work and Rehabilitation; Institute of In-Service Education Borys Hrinchenko Kyiv Metropolitan University, the Department of Science and Mathematics Education and Technologies (B); Department of Socio-Humanitarian and Legal Disciplines of the Faculty of State Security of the Kyiv Institute of the National Guard of Ukraine (C). The sample size was 140 people, who were divided into two groups – the EG and CG. The groups were distributed evenly with the same conditions (Table 1).
Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of participants (N = 140)